We recently tested the NVIDIA DGX Spark™. This desktop AI supercomputer, similar in size to a Mac mini, packs enterprise-grade GPU performance into a compact box. Together with the Dify AI application development platform, it offers enterprises an end‑to‑end private AI deployment solution.
By combining Dify and DGX Spark, organizations can run AI agents entirely on‑premises. From data ingestion and model inference to application delivery, the pipeline stays within your local environment, ensuring data security and compliance.
 |  |
From Hardware to Infra: A Fully Integrated Stack
The combination of Dify and DGX Spark provides an integrated stack from hardware to infrastructure:
Hardware: DGX Spark brings together the full NVIDIA AI platform — including GPUs, CPUs, networking, CUDA® libraries and the NVIDIA AI software stack. DGX Spark is powered by the NVIDIA GB10 Grace Blackwell Superchip, featuring 128 GB unified memory and up to 1 petaflop of FP4 AI compute. It supports local inference for open-source models like Llama 3, Qwen 2.5, DeepSeek V3, and NVIDIA’s own models (Nemotron, NVIDIA NIM).
Platform: On top of that, the Dify platform offers:
Visual Workflow orchestration
Integrated Knowledge pipeline.
Unified multi-model management
With this stack, enterprises can build AI Agents without code, while keeping the full lifecycle—data input, model inference, and application output—within the local environment.

NVIDIA DGX Spark: Desktop AI Compute
Launched on October 15, the DGX Spark removes the traditional need for cloud infrastructure or large data center servers for AI deployment. It gives AI developers, SMBs, and research institutions an accessible, on‑premises compute option.
Key specifications:
GB10 Grace Blackwell Superchip
20‑core Arm CPU
Blackwell Architecture GPU
128 GB unified memory
Up to 1 PFLOP of FP4 AI compute
Runs models up to 200B parameters (single device)
Supports up to 405B parameters (two interconnected devices)
Developers can deploy models and build apps directly from their desk, keeping data and computation local.
Building a Private AI Agent with Dify and DGX Spark
Teams can rapidly build private AI Agents by combining Dify’s application platform with DGX Spark’s compute.
Architecture Overview
The architecture consists of four layers, creating a closed loop from hardware to business apps:
Hardware Layer: NVIDIA DGX Spark provides on-premises GPU compute and unified memory, supporting large-scale model loading and high-performance inference.
Inference Layer: Local Large Models Deploy mainstream open-source models such as Llama 3, Qwen 2.5, DeepSeek V3 together with NVIDIA's own models like Nemotron-4; expose inference APIs through Ollama, vLLM, or TensorRT-LLM.
Application Layer: Dify Platform Offers visual workflow orchestration, integrated RAG knowledge bases, multi-model routing and management, and zero-code AI application development.
Business Layer: Enterprise AI Agents Supports real-world use cases including intelligent customer service, R&D copilots, data analysis assistants, and other domain-specific AI Agents.
Implementation Steps
1. Environment Preparation
Install Docker on DGX Spark and ensure Docker Engine is running.
2. Deploying Dify on DGX Spark
For full instructions, refer to the official Dify docs.
Basic steps:
git clone https://github.com/langgenius/Dify.git
cd Dify/docker
cp .env.example .env
docker compose up -d
Once containers are running, go to http://localhost/install. (If running on a remote server, replace localhost with the server’s IP).
3. Deploying Local Models and the Inference Engine
For detailed model deployment instructions, refer to the official NVIDIA DGX Spark documentation.
We will deploy a TensorRT-LLM environment to serve large models on the local GPU.
Key steps:
Initialize Runtime: Verify Docker permissions, GPU drivers, and the container runtime so Spark recognizes the local GPU.
Configure Environment Variables and Caching: Set up a Hugging Face token and a local cache directory to avoid repeated downloads.
#Create Hugging Face cache directory mkdir -p $HOME/.cache/huggingface/
Verify the TensorRT‑LLM: Use the NVIDIA container image to verify the environment. Example using
Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP4:
export MODEL_HANDLE="nvidia/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP4"
docker run \ -e MODEL_HANDLE=$MODEL_HANDLE \ -e HF_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN \ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/:/root/.cache/huggingface/ \ --rm -it --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 \ --gpus=all --ipc=host --network host \ nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt-llm/release:spark-single-gpu-dev \ bash -c ' hf download $MODEL_HANDLE && \ python examples/llm-api/quickstart_advanced.py \ --model_dir $MODEL_HANDLE \ --prompt "Paris is great because" \ --max_tokens 64 '
This downloads the model, initializes the runtime, and runs a test prompt.
Model Support on DGX Spark
DGX Spark supports many mainstream models, including:
Llama 3.1 FP4
GPT-OSS 20B
Qwen 2.5-VL 7B
Starting a Local Inference Service
Once the environment is validated, launch a persistent service using trtllm-serve. We will use Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP4 as the example:
export MODEL_HANDLE="nvidia/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP4"
docker run --name trtllm_llm_server --rm -it --gpus all --ipc host --network host \ -e HF_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN \ -e MODEL_HANDLE="$MODEL_HANDLE" \ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/:/root/.cache/huggingface/ \ nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt-llm/release:spark-single-gpu-dev \ bash -c ' hf download $MODEL_HANDLE && \ cat > /tmp/extra-llm-api-config.yml <<EOF print_iter_log: false kv_cache_config: dtype: "auto" free_gpu_memory_fraction: 0.9 cuda_graph_config: enable_padding: true disable_overlap_scheduler: true
EOF
trtllm-serve "$MODEL_HANDLE" \ --max_batch_size 64 \ --trust_remote_code \ --port 8355 \ --extra_llm_api_options /tmp/extra-llm-api-config.yml '
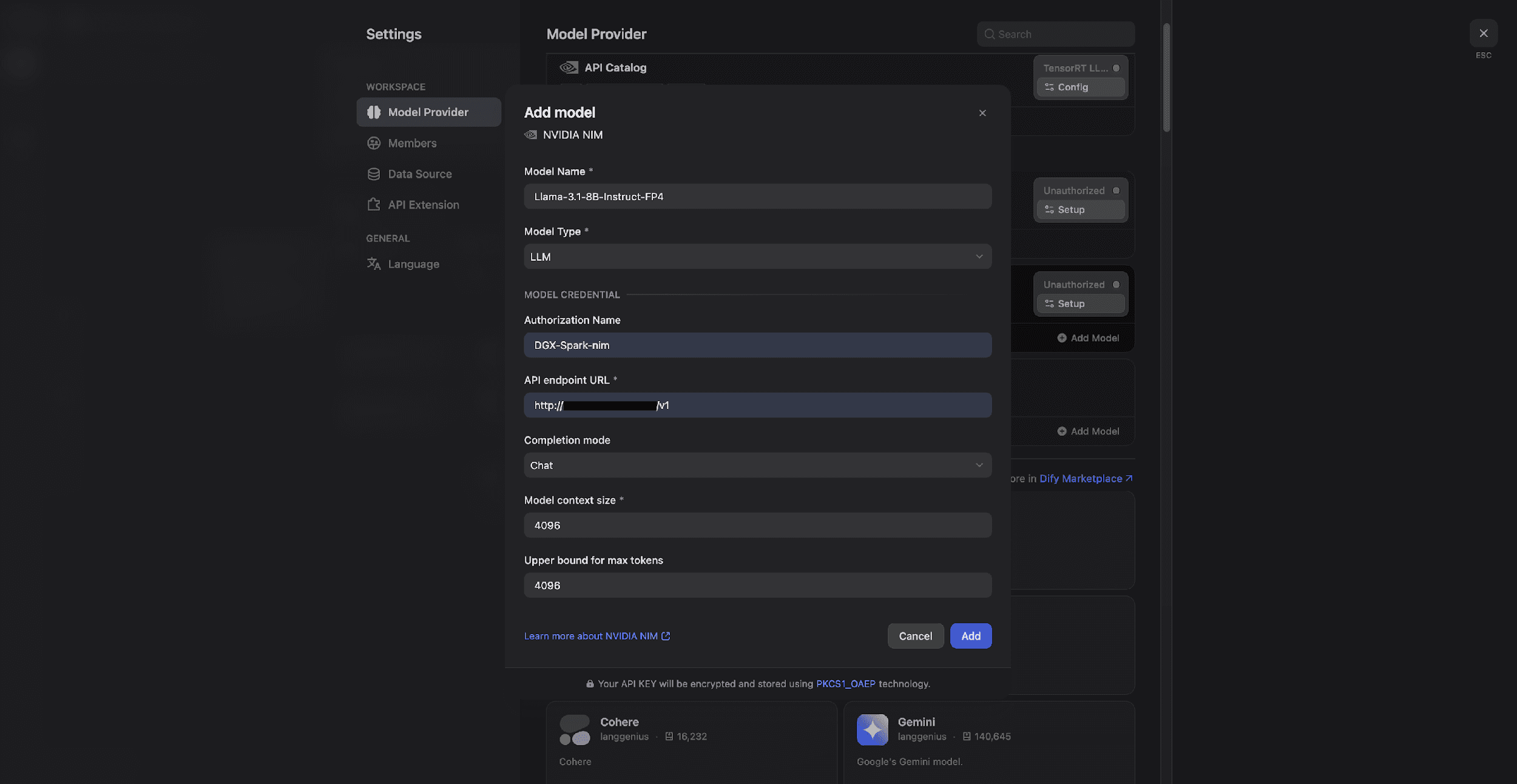
4. Connect the model to Dify
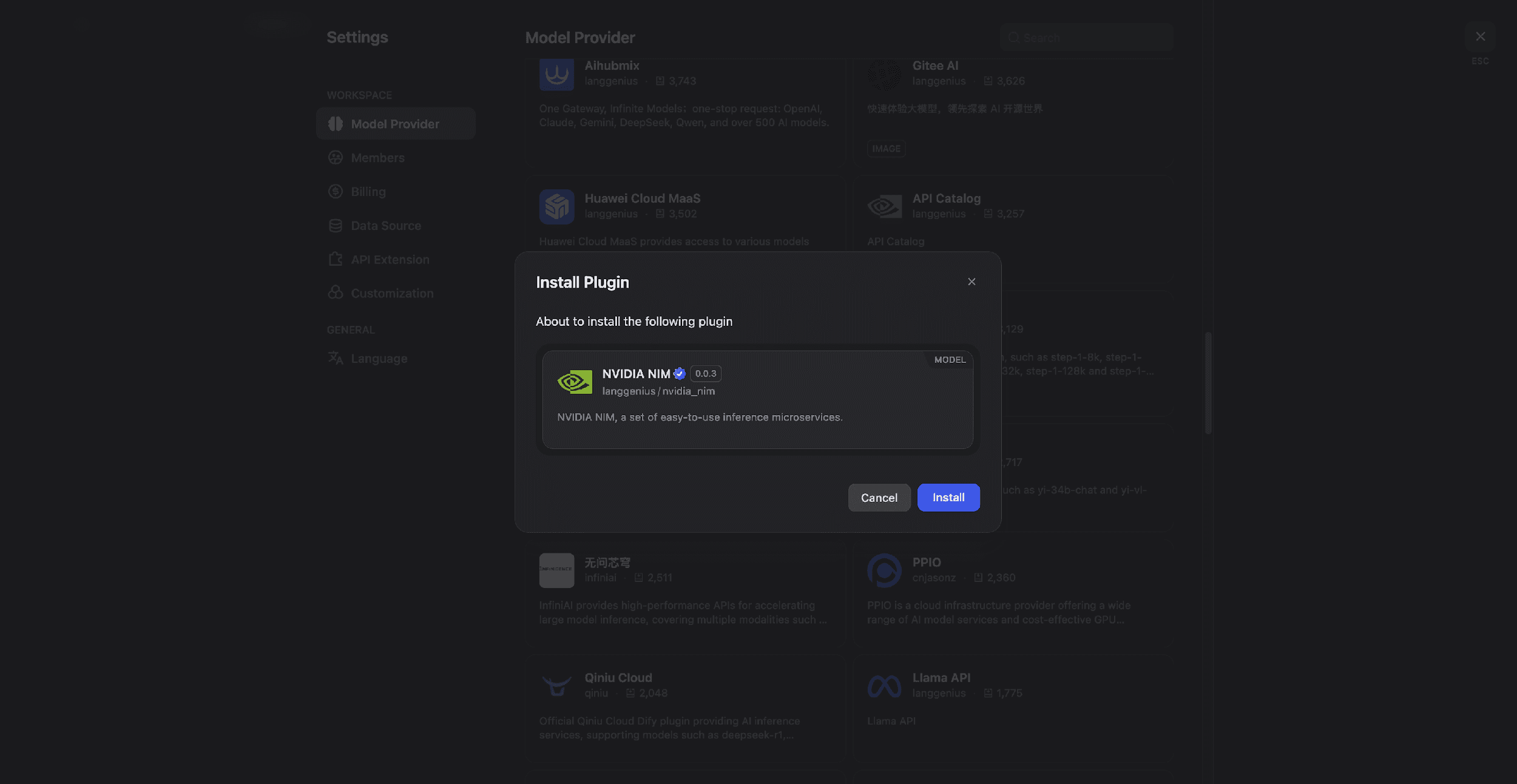
1) Go to Dify Settings → Model Provider.
2) Search for NVIDIA NIM and install the plugin.
3) Enter the credentials:
Model name: e.g., Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-FP4
API URL: Use the default or the address from your .env file.
5. Building AI Applications with Dify
Start by choosing an application type: Chatflow is designed for multi-turn conversational experiences. Workflow automates complex business processes. Agent handles intelligent tasks that require autonomous decision-making and tool invocation. All three support a zero-code approach, so teams can move from idea to production-ready application quickly. In the previous steps, we have already deployed and validated the local inference service on DGX Spark. Next, select an appropriate application template in Dify to quickly set up a sample application that connects to your business needs.
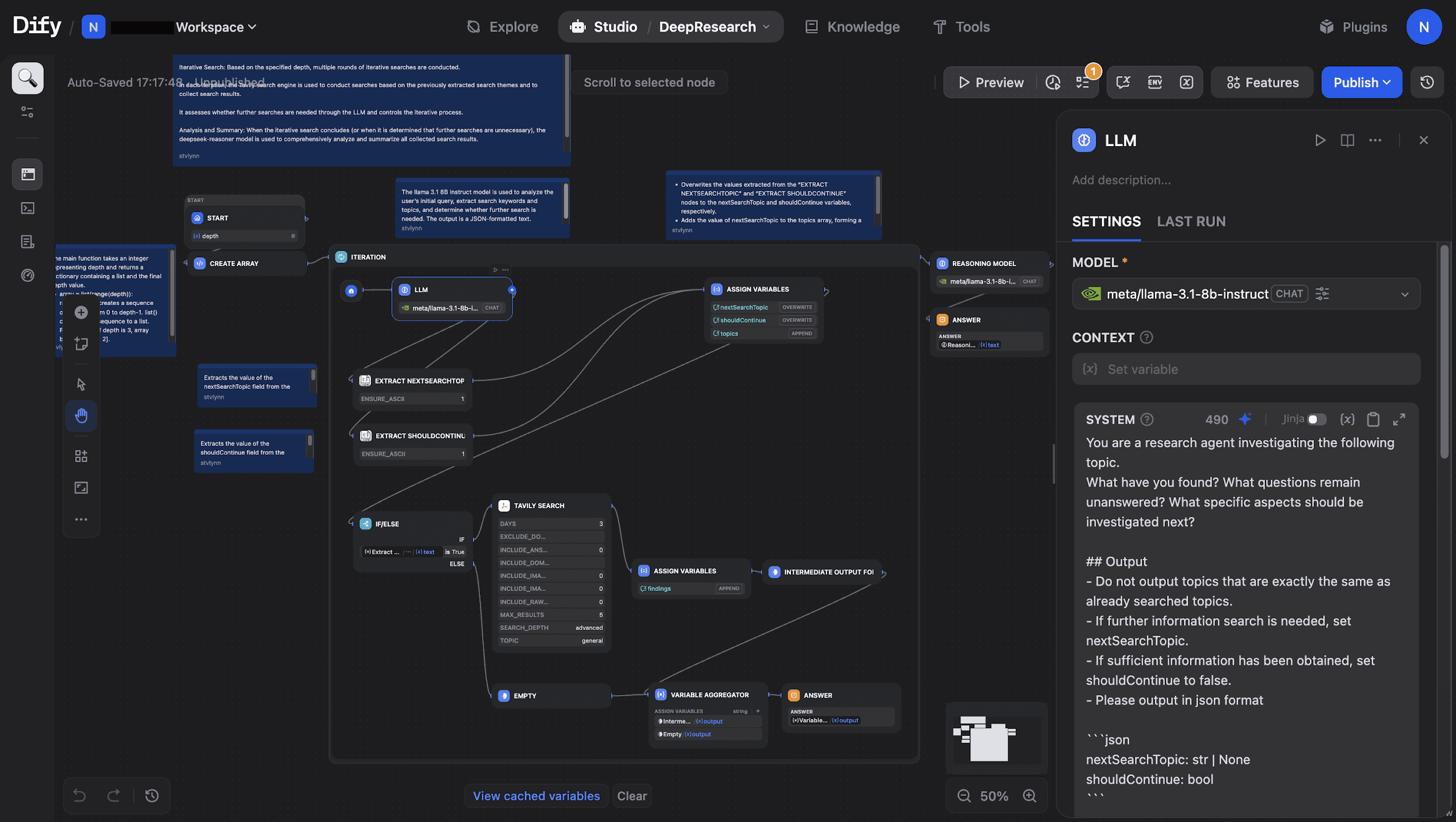
Example: Deep Research Workflow
We will use the Template Marketplace to create a Deep Research workflow. The template comes with a prebuilt core path covering LLM inference, search initialization, iterative search, and analytical summarization. Based on the user's question and the desired research depth, it automatically executes a complete research pipeline: Parse → Search → Iterate → Reason → Report Generation. This makes it well suited for professional scenarios such as technology selection, industry research, and complex problem analysis.
In this workflow, the LLM node acts as the "brain." We configure this node to run Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct on DGX Spark, enabling deeper local analysis.
6. Production Deployment
After the application is built, it can be released with just one click and go live. Whether accessed through the API to integrate with the business system or directly embedded in the website, Dify provides developers with a ready-to-use environment. From data processing and model inference to application operation, the entire process runs on DGX Spark in a closed loop. Data stays within the local network, meeting enterprise data security and compliance requirements. Once developed, the AI application can go straight to production to deliver stable AI capabilities for the business.
Application Paths and Usage Scenarios
As more teams build workflows in Dify, fine-tune models, and use RAG retrieval and reasoning services, Spark provides a compute environment that closely matches developer needs and accelerates a wide range of AI workloads.
Prototyping: Closing the Loop and Iterating in Dify
When teams use Dify for prototype design, testing application logic, or validating Agent capabilities, they can run different model architectures and datasets locally on Spark to quickly complete an end-to-end experimental loop. Whether it’s multi-step reasoning in a Workflow, recall testing for the RAG module, or plugin/tool invocation logic, teams can iterate rapidly on Spark.
Model Fine-Tuning: Building Your Own Private Models for Dify
DGX Spark comes with 128GB of memory, which is sufficient to support fine-tuning models up to roughly 70B parameters. This means users can fine-tune open-source large models (such as the Llama family) directly on Spark for specific tasks, allowing custom models to learn from their own datasets and achieve inference behavior that better fits business scenarios. After fine-tuning, these models can be uniformly integrated into existing Workflows, RAG knowledge bases, and Agent applications through Dify’s multi-model management capabilities, forming a truly “end-to-end self-owned model system” that can be continuously reused and iterated within the enterprise.
Local Inference: Building Your On-Premises Private Data Center
Spark supports FP4/FP8 inference acceleration for 200B-parameter-class models, delivering up to 1 PFLOP of local FP4 AI performance. In Dify practice, this means teams can run high-performance inference locally, with the entire process—from data ingestion and model inference to output delivery—completed in a closed loop within the enterprise intranet. This keeps sensitive data fully on-premises while enabling teams to continuously build and operate their own AI Agents with lower overall cost and greater controllability.



