
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique that combines large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge sources. It allows LLMs to retrieve relevant documents and use them as context to answer user queries more accurately.
In a typical traditional RAG pipeline, the system embeds the user query, performs a vector similarity search in a knowledge base (e.g., via a vector database), and then passes the top-k retrieved documents to the LLM for answer generation. While this reduces hallucination and grounds responses in factual data, it has clear limitations: the retrieval process is one-shot, lacks reasoning, and cannot adjust dynamically if the results are poor.
What Is Agentic RAG?
Agentic RAG addresses these limitations by embedding retrieval inside an intelligent reasoning loop. Instead of treating retrieval as a fixed preprocessing step, it makes it part of an agent’s decision-making process. The agent — powered by an LLM — analyzes the query, plans its approach, selects tools and sources, evaluates retrieved content, and retries or switches strategies when needed.
This dynamic retrieval approach transforms RAG into a flexible and adaptive framework that can handle ambiguous or multi-step tasks more effectively. Agentic RAG systems are especially well-suited to scenarios requiring reasoning across multiple sources or where the quality of initial retrievals must be validated before generation.
Traditional RAG vs Agentic RAG
Traditional RAG | Agentic RAG | |
Retrieval logic | One-shot | Multi-step, iterative |
Tool flexibility | Fixed retriever | Multiple tools with dynamic selection |
Reasoning | None | Yes |
Query refinement | No | Yes |
Result evaluation | No | Yes (feedback loop) |
Answer reliability | Relies on initial search | Improved through iteration |
How Agentic RAG Works
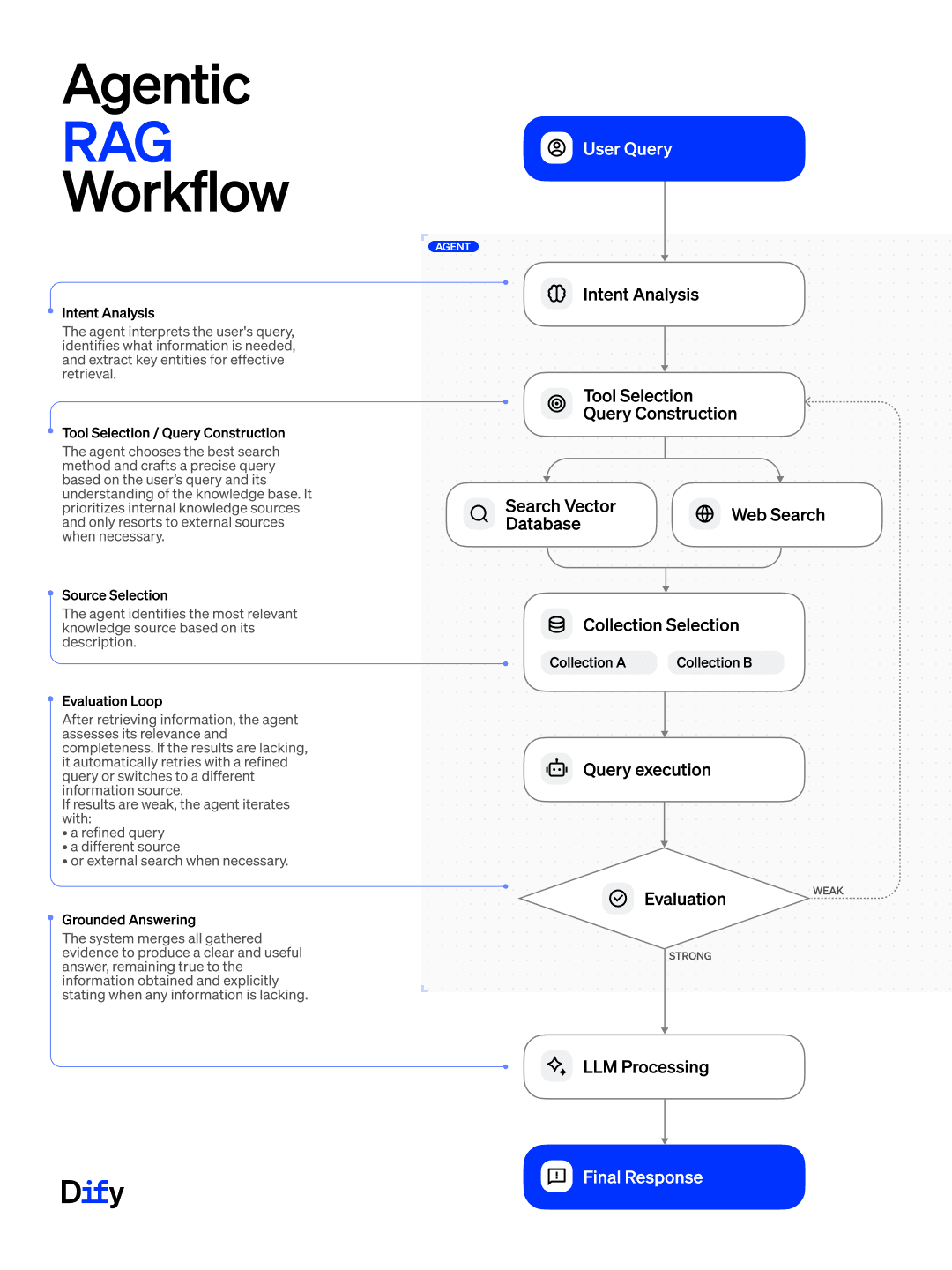
Agentic RAG introduces reasoning into each phase of retrieval. A typical workflow includes the following steps:
Intent Analysis The agent interprets the user query to understand what type of information is needed. It extracts key concepts and entities and infers the search objective.
Tool Selection & Query Construction Based on the query type, the agent selects the most appropriate search method (e.g., vector search, hybrid, keyword, or web). It then constructs an optimized query adapted to the chosen tool.
Source / Collection Selection If multiple collections exist, the agent determines which is most relevant based on metadata, schema, or prior experience. It routes the query accordingly.
Query Execution The selected tool and collection are used to retrieve candidate documents. These are ranked and passed back to the agent.
Evaluation Loop The agent assesses the quality of the retrieved documents. If coverage is insufficient or irrelevant, it refines the query, switches tools, or tries a fallback (e.g., web search). This loop continues until results are satisfactory or iteration limits are hit.
Grounded Answer Generation Only after confirming that the evidence is strong does the system proceed to answer generation. The final output is grounded in validated, relevant content.
This approach ensures that retrieval is not a blind process, but a guided, adaptive step informed by reasoning and evaluation.
How Dify Enables Agentic RAG
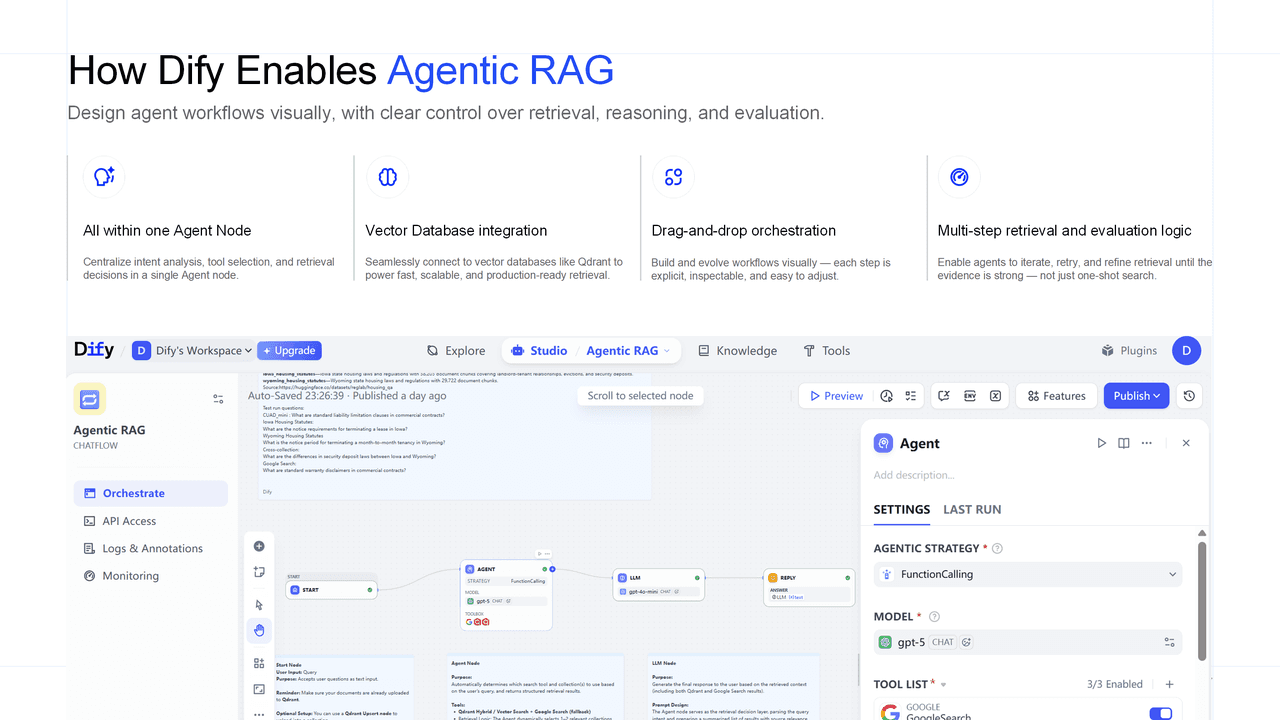
Dify provides a practical framework to implement Agentic RAG through:
Agent Node: A centralized decision engine that combines intent analysis, tool orchestration, source selection, and retry logic. It encapsulates all agent behavior.
Drag-and-Drop Workflow Builder: Users can create complex multi-step workflows visually, with each reasoning or action step as a node.
Native Tool Integration: Qdrant (vector & hybrid search), Google Search, and custom APIs are supported as tools.
Iteration Support: Built-in strategy support allows agents to retry, refine, or fall back dynamically. Developers can define behavior using strategies like Function Calling or ReAct.
By consolidating all retrieval logic in a single node, Dify makes Agentic RAG workflows transparent, reusable, and easy to evolve.
Use Cases
Agentic RAG excels when:
The query is ambiguous, multi-step, or lacks sufficient initial context.
Retrieval needs to span different formats, domains, or sources.
Reasoning, decision-making, or fallback behavior is required.
Some representative use cases:
Enterprise Knowledge Assistant: Routes complex employee queries across HR documents, internal wikis, and product policies. Example: “Can remote employees in California expense coworking space?”
Legal or Scientific Research Assistant: Retrieves information from structured datasets, academic papers, and regulatory guidelines to support fact-checking or cross-jurisdictional comparisons.
Developer Copilot: Queries internal code repositories, documentation, and build/test results; optionally runs tools like linters or static analysis.
AI Workflow Assistants: Combines retrieval with actions like summarization, formatting, or emailing results, useful in operations and team workflows.
Customer Support Agents: Search across CRM, product manuals, support tickets, and optionally escalate or re-ask based on incomplete responses.
These use cases benefit from Agentic RAG’s ability to adapt and self-correct across multiple knowledge boundaries.
Limitations to Consider
Latency: Multi-step reasoning and retries naturally increase response time.
LLM Reasoning Quality: Agents may make suboptimal decisions, especially if prompts are poorly designed.
Higher Cost: Iteration and multiple tool calls increase token usage and compute cost.
Operational Complexity: Requires thoughtful prompt engineering, retry limits, and fallback rules to avoid loops or tool misuse.
Agentic RAG introduces new challenges in control and reliability, which must be handled with guardrails, logging, and strategy design.
Conclusion
Agentic RAG represents a shift from static retrieval to dynamic decision-driven knowledge access. By embedding retrieval into a reasoning process, it enables systems to adapt, iterate, and verify — ultimately improving answer quality.
With tools like Dify, teams can build such systems visually and modularly. Agentic RAG workflows are especially useful when trust, precision, or contextual flexibility is required. As LLMs move from passive responders to autonomous agents, Agentic RAG will be a key enabling pattern.
For a more detailed walkthrough of Agentic RAG and its implementation in Dify, see this webinar:






