Enterprise knowledge has never been limited to text. Product manuals contain real-world photos, technical reports include architecture diagrams, and training guides are filled with UI screenshots. The information density and importance of these visual assets often equal or exceed that of the text itself.
While multimodal embedding capabilities have existed for some time, few products have successfully integrated them into practical knowledge base solutions. Traditionally, enterprises had to either build complex cross-modal pipelines, processing images and text separately before attempting to merge them, or ignore images entirely, relying solely on text retrieval. Both approaches have significant limitations.
Now, the Dify Knowledge Base officially supports multimodal capabilities. Text and images can be understood, retrieved, and utilized together within Workflow applications. The context retrieved by AI Agents is no longer restricted to text; they can now "see" images, interpret the information within them, and provide answers accordingly.
Core Breakthrough: A Unified Semantic Space
Starting from Dify v1.11.0, we have introduced multimodal embeddings within a unified semantic space. By placing images and text into a shared coordinate system, we have enabled "Image-to-Text," "Text-to-Image," and "Image-to-Image" retrieval, significantly improving search accuracy.
Multimodal Support: The system automatically extracts images referenced via Markdown links (supporting JPG, PNG, and GIF, up to 2MB). When a multimodal embedding model is selected, these images are vectorized and stored alongside text for retrieval.
Broad Model Ecosystem: Dify supports multimodal embedding and rerank models from various cloud providers and open-source ecosystems, including AWS Bedrock, Google Vertex AI, Jina, and Tongyi. Models with multimodal capabilities are now marked with a VISION badge in the settings panel for easy identification.
From "Semantic Matching" to "Visual Understanding"
Intuitive Intent Capture: Users can describe their needs through natural language or by uploading relevant images. The system retrieves both semantically related text and images to help users locate key information quickly.
Complete RAG Reasoning: When using a Vision-enabled LLM, the AI is no longer limited to text citations. It can incorporate relevant images into the reasoning process and explain details found within them, resulting in more accurate and helpful answers.
Technical Value: Why RAG Requires Embedding and Rerank Synergy
In a broad RAG architecture, information moves through a pipeline of "Chunking - Indexing - Retrieval - Reranking - Generation." This process transforms scattered documents into a precise information flow. Within this framework, Embedding and Reranking are both essential:
Multimodal Embedding maps content into a vector space to perform the first round of fast similarity matching. It determines whether your query can accurately locate relevant content within a massive knowledge base.
Multimodal Reranking evaluates the specific relevance between the query, text, and images. It ensures that the most critical visual and textual evidence is prioritized, providing the LLM with the most accurate context.
The true value of these capabilities lies in making images searchable, rankable, and actionable evidence. In enterprise RAG and Agentic Workflows, this expands the boundaries of document processing. Product specs, diagrams, and screenshots are no longer just "decorations"—they are now computable knowledge.
Example Scenario: A “Look at the Image and Answer” Assistant
Users can now describe a problem and upload a photo to trigger an integrated "Retrieve - Identify - Analyze - Answer" workflow.
Step 1: Create a Multimodal Knowledge Base
Importing Documents:
Create a new knowledge base and upload your "Product Manual."
Configuration:
Select an Embedding and Rerank model with the VISION badge. You will see that images in the preview area are processed immediately.
Managing Image Chunks:
Images can be managed at the chunk level. If a multimodal embedding model is used, images are vectorized and directly involved in retrieval; if a text-only model is used, images are returned only as attachments when their corresponding chunks are retrieved.
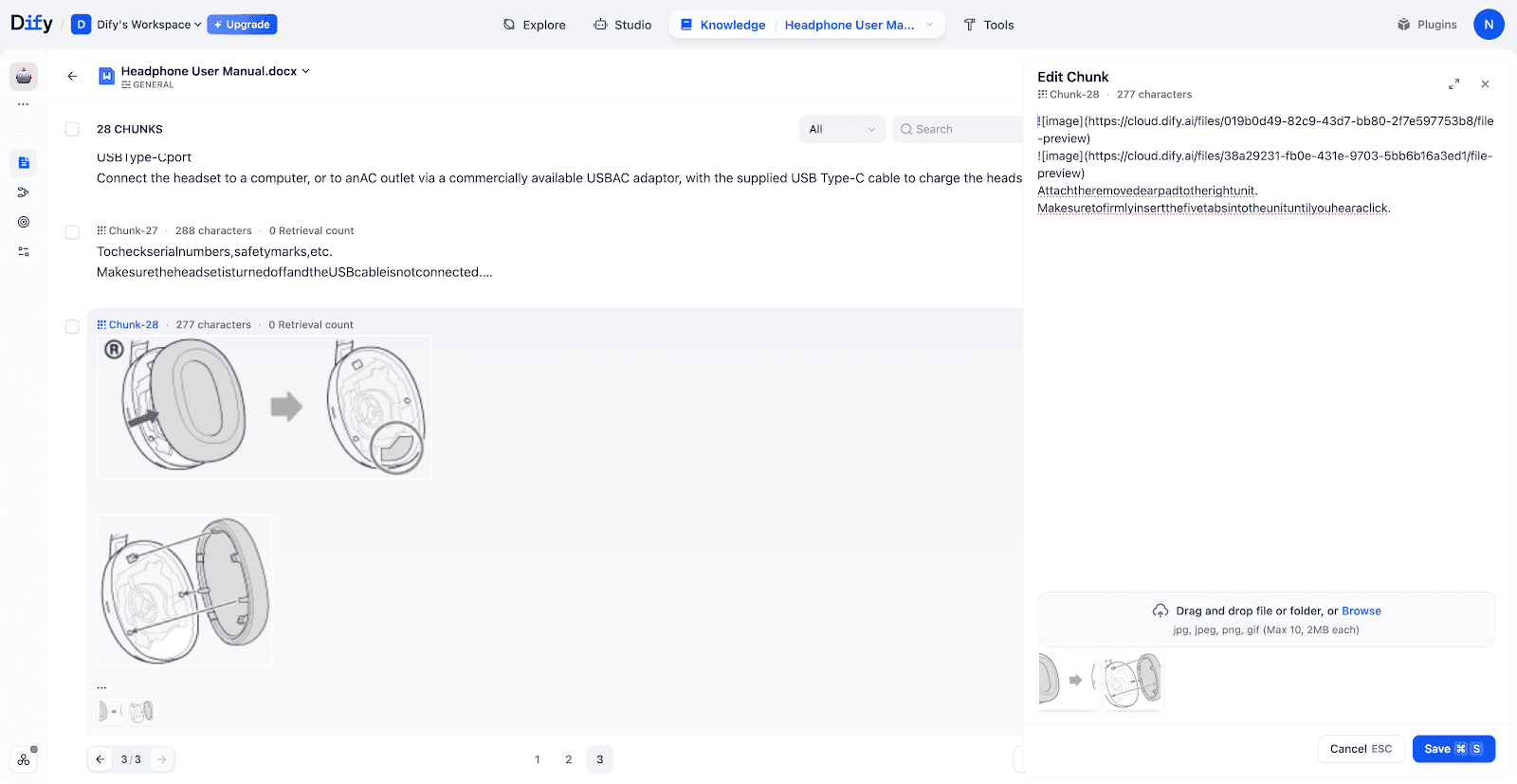
Testing Retrieval:
In this tests, uploading a photo of a pair of headphones successfully retrieved the corresponding manual chapters, including structural diagrams and accessory lists.
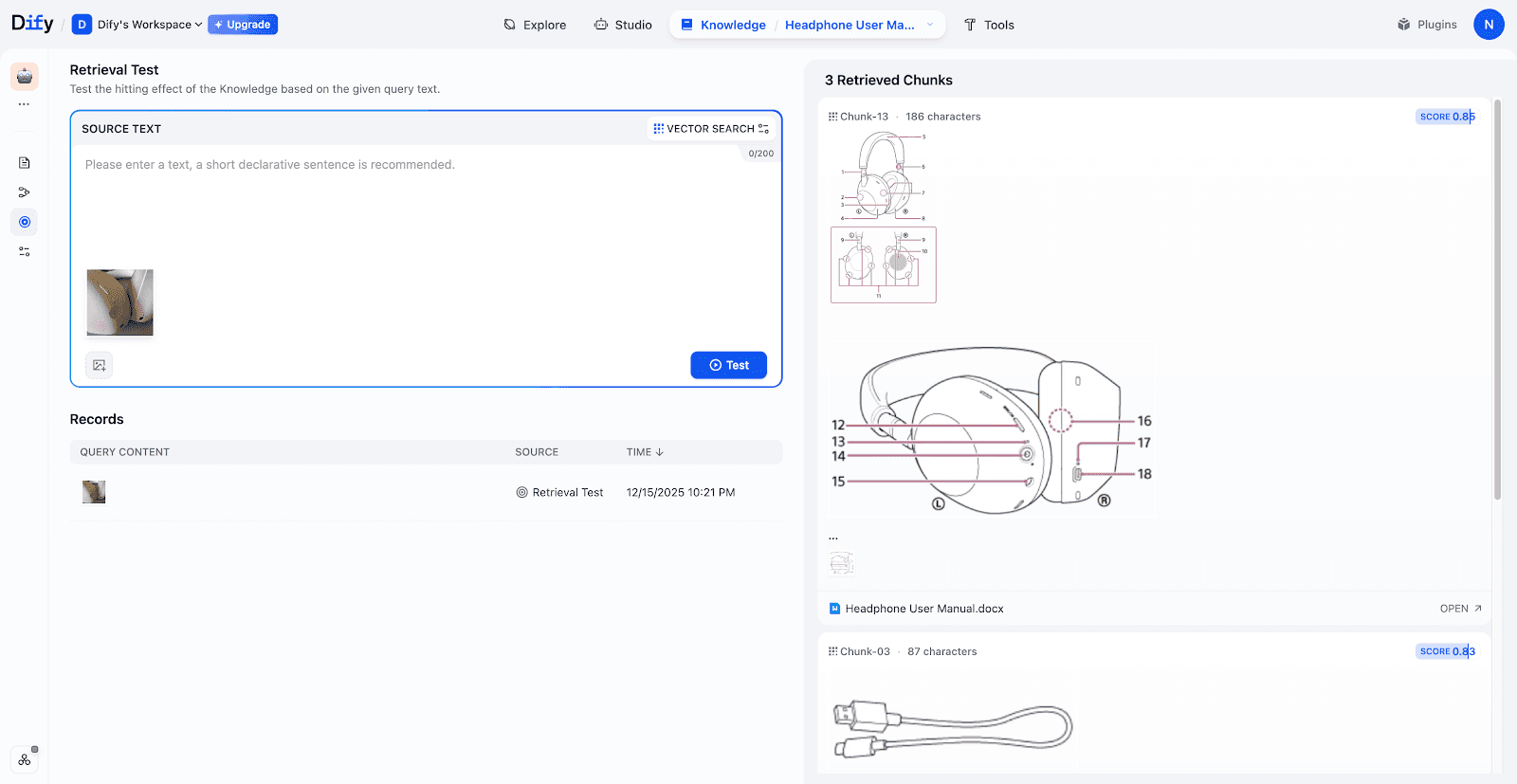
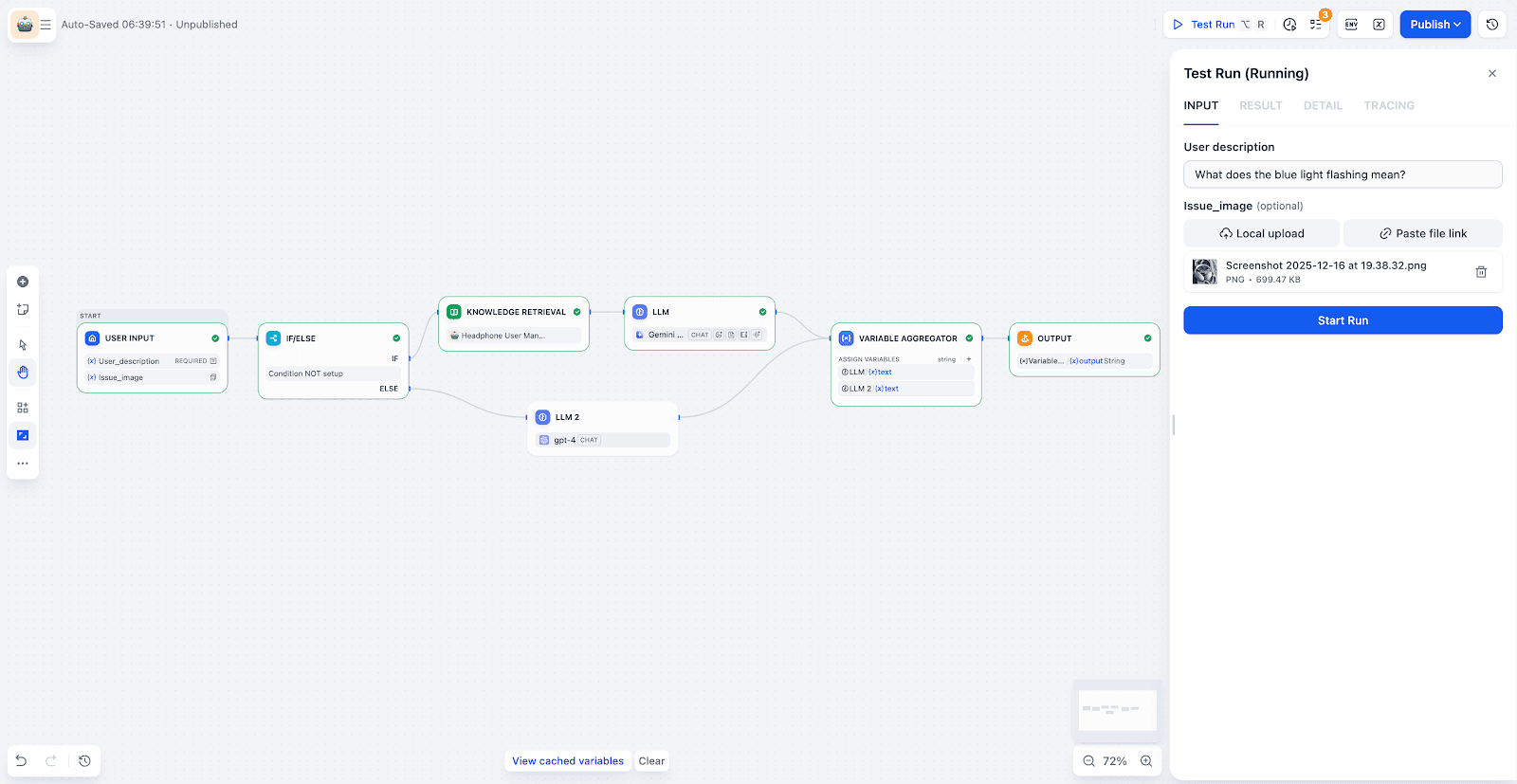
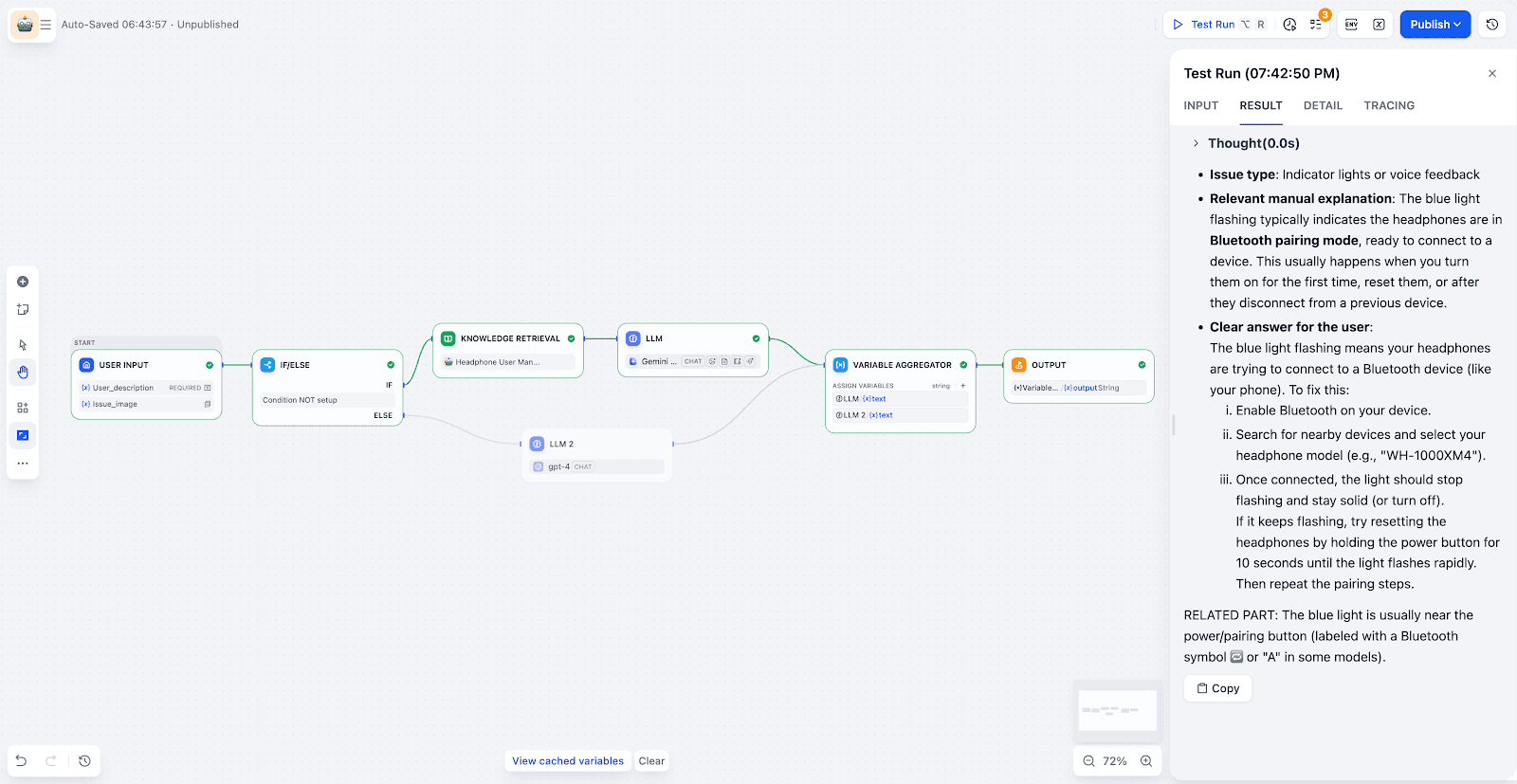
Step 2: Building a Workflow for Automated Queries
Input & Branching:
The workflow receives the user's question and image. A "IF/ELSE" node determines if the query can be answered by the knowledge base or if it should be routed elsewhere (e.g., a manual support ticket).
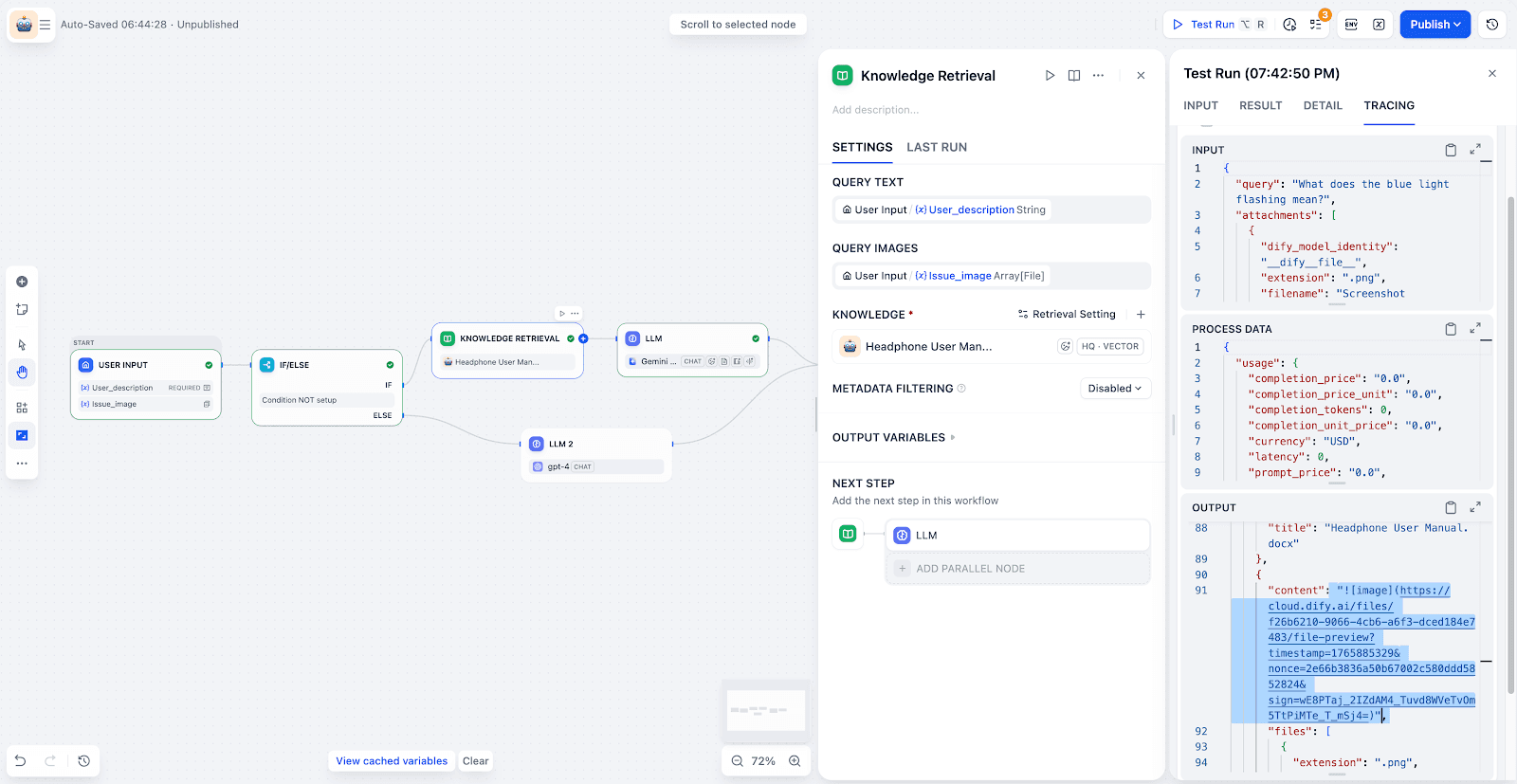
Knowledge Retrieval:
The system searches the knowledge base to find the most relevant text and image chunks.
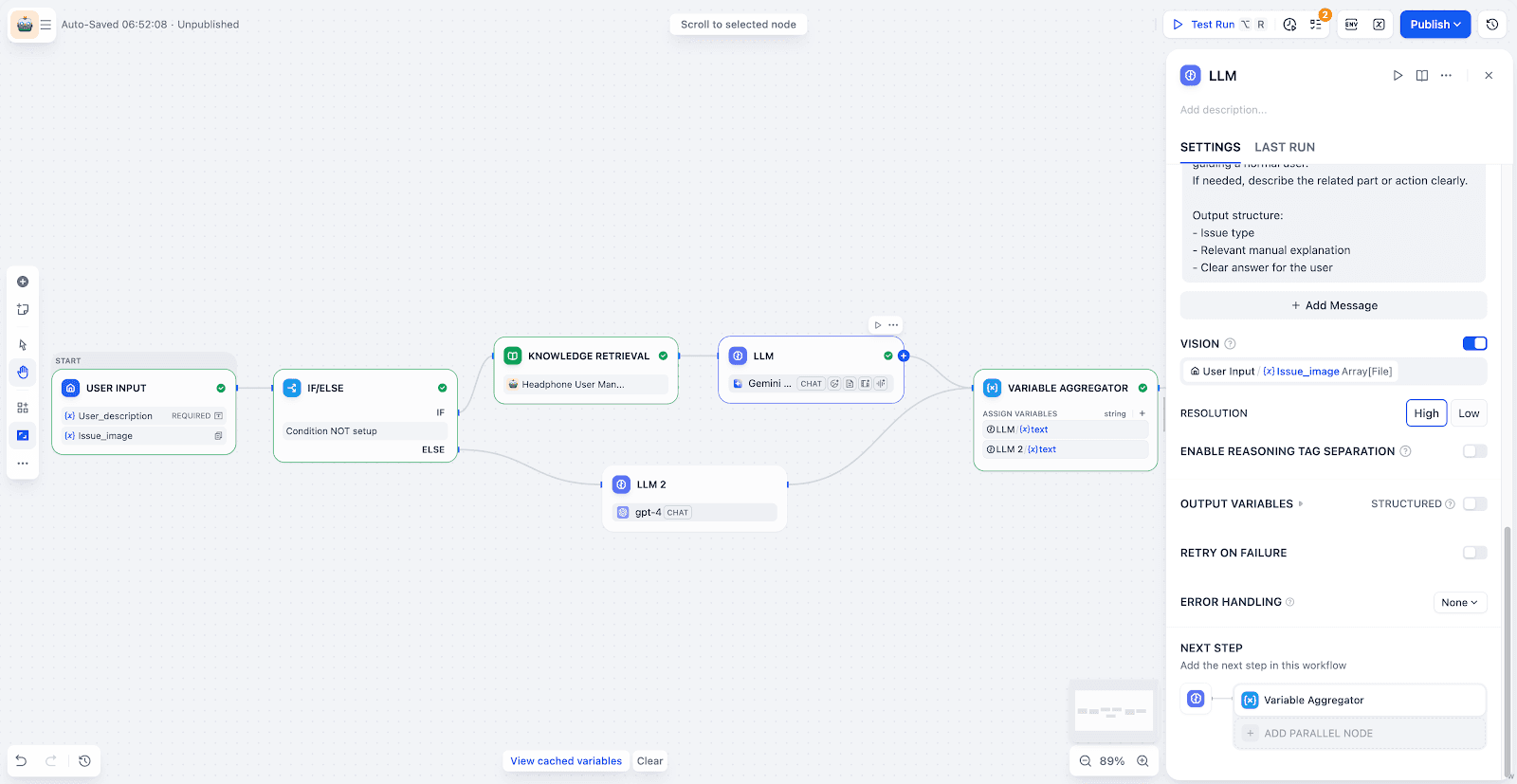
LLM Node with Vision:
Enable Vision mode, and select the uploaded image variable. The LLM can then extract key information from the image. It can combine that with the task requirements to analyze and locate the problem.
Aggregation & Output:
Finally, use a variable aggregation node to merge:
the retrieval results
the LLM analysis
Then output a clear and actionable answer.
Conclusion: From Text Search to Intelligent Execution
The launch of the Multimodal Knowledge Base marks Dify’s evolution from a text-based retrieval tool to a comprehensive enterprise knowledge and automation platform.
This is not only about “reading” an image.
It is about turning visual information into Workflow context. That context can then support reasoning and actions. Whether you need to query technical practices, send automated notifications, or drive complex business Workflows, your Agent can move from passive Q&A to real decision‑making and execution.
It becomes a system that is practical, reliable, and ready for real enterprise use.



